About:
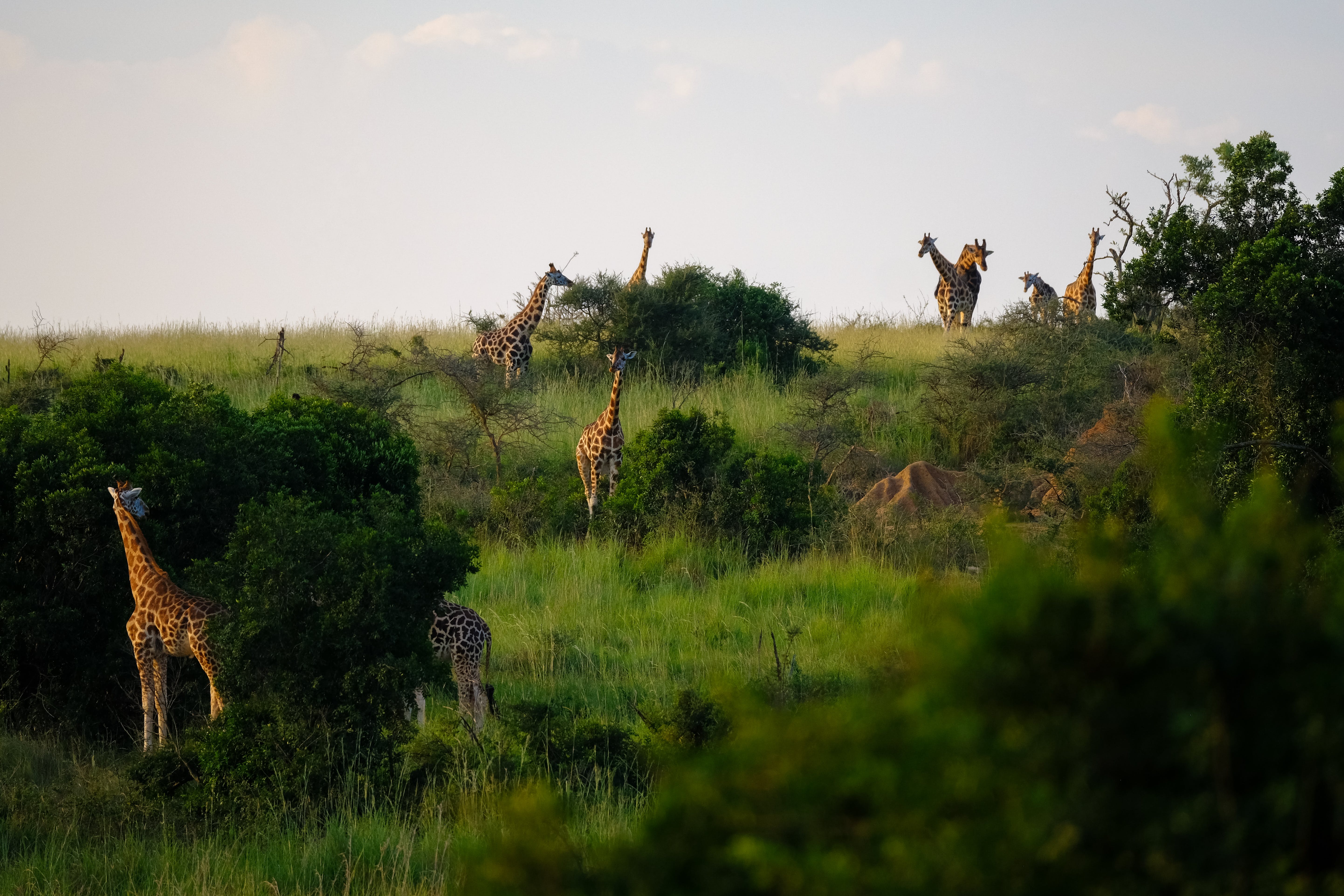
Giraffes (Giraffa camelopardalis) are native to the African continent and are primarily found in savannas, grasslands, and open woodlands. Here is an in-depth discussion about the locations where giraffes are commonly found:
Africa Raange:
Giraffes are naturally distributed across various African countries, with the highest populations found in East Africa. Some of the countries where giraffes are commonly found include:
Kenya:
Kenya is renowned for its diverse wildlife, and giraffes are no exception. The country's national parks and reserves, such as Maasai Mara and Amboseli National Park, provide suitable habitats for giraffes.
Tanzania:
Tanzania's iconic Serengeti National Park and Ngorongoro Conservation Area are home to sizable giraffe populations. These areas offer vast grasslands and woodlands, which are ideal giraffe habitats.
South Africa:
Giraffes are found in several game reserves and national parks in South Africa, including Kruger National Park. These protected areas offer a mix of savannas and thorny scrublands, which are suitable environments for giraffes.
Namibia:
Giraffes are found in parts of Namibia, particularly in the Etosha National Park, where they roam the arid savannas and dry woodlands.
Botswana:
Giraffes can be spotted in various wildlife reserves and national parks in Botswana, such as Chobe National Park, where they inhabit riverine woodlands and grassy plains.
Uganda:
Giraffes are found in some of Uganda's national parks, including Murchison Falls National Park, where they inhabit savannas and acacia woodlands.
Habitat Perferences:
Giraffes are highly adaptable and can survive in different types of habitats within the regions they inhabit. They prefer areas with scattered trees and bushes, which provide both food and some shelter. Giraffes have a unique feeding strategy, as their long necks enable them to reach high branches and foliage that other herbivores cannot access, allowing them to thrive in semi-arid regions with limited vegetation.
Conservation Challenges:
Despite their wide distribution, giraffes face significant conservation challenges. Habitat loss due to human activities such as agriculture, logging, and infrastructure development is a major threat. Additionally, poaching, climate change, and human-wildlife conflict further endanger giraffe populations. Conservation organizations and governments are working together to address these challenges, establish protected areas, and raise awareness to ensure the survival of giraffes in their natural habitats.